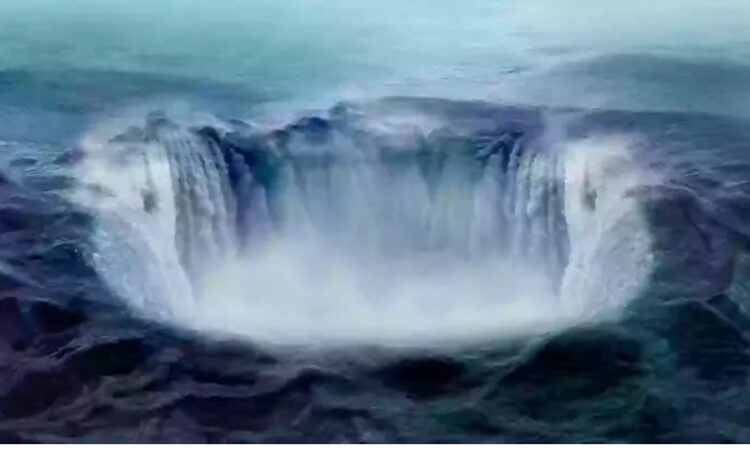
Scientists have made significant progress in understanding the mystery behind the massive ‘gravity hole’ in the Indian Ocean, known as the Indian Ocean Geoid Low (IOGL).
This anomaly, first discovered in 1948 by Dutch geophysicist Felix Andries Vening Meinesz, spans 1.2 million square miles and causes a 328-foot dip in sea level. For decades, the IOGL puzzled researchers due to its unusual gravitational pull, which is weaker than surrounding areas.
In 2023, a team of researchers from the Indian Institute of Science in Bengaluru and the GFZ German Research Centre for Geosciences proposed a credible explanation.
They suggest that plumes of magma rising from deep within the Earth are responsible for creating this ‘gravity hole.’ To test this hypothesis, the team used supercomputers to run 19 simulations, recreating Earth’s formation over the past 140 million years. Their findings were published in the journal *Geophysical Research Letters* in May 2023.
According to the study, Earth’s density is not uniform, with some areas being denser than others. This uneven distribution affects the planet’s surface and gravity. Attreyee Ghosh, the study’s co-author, explained that the Earth is not a perfect sphere but an ellipsoid due to its rotation, which causes the middle to bulge outward.
The plumes of magma are believed to have originated from the disappearance of an ancient ocean that once existed between the Indian and Asian tectonic plates.
As India drifted northward and collided with Asia tens of millions of years ago, the ocean vanished, and the movement of tectonic plates likely contributed to the formation of the IOGL.
This breakthrough provides a clearer understanding of the geological processes behind the ‘gravity hole’ and highlights how Earth’s dynamic interior shapes its surface and gravitational field.
The study underscores the importance of advanced simulations and interdisciplinary research in solving long-standing scientific mysteries.